Application of Artificial Photosynthesis Performed by Copper-decorated WO3
呂之甯、陳品妤、陳葦庭
Abstract
With the significant advantages of using sunlight as the reaction energy source, photocatalyst has been viewed as a promising solution to excessive carbon dioxide emissions. Due to the high stability of linear structure, carbon dioxide possesses high bonding energy (~532 kJ/mol). Photocatalyst can lower LUMO (Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital) of carbon dioxide by providing electrons to CO2, which has a positive effect on the photocatalytic conversion and turns CO2 into solar fuels.
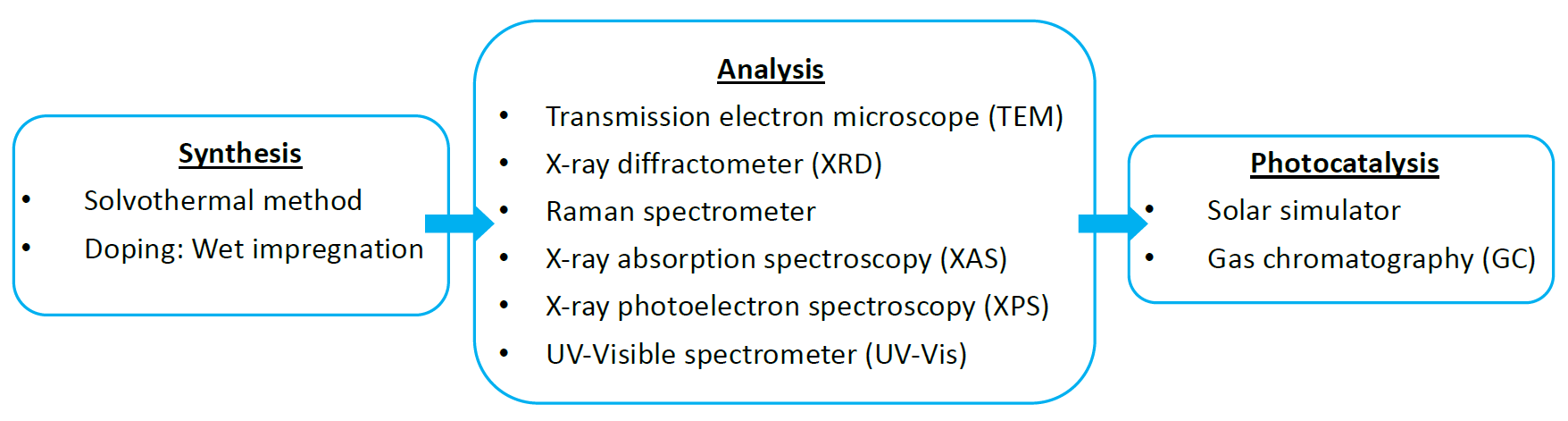
In this research, we focus on doping Cu atoms on the surface of tungsten trioxide (WO3) to capture more electrons and enhance the reaction activity. We use transmission electron microscope (TEM) to observe the crystal. We also use Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffractometer (XRD) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) to confirm how Cu is introduced into WO3. Then, we operate UV/Visible Spectrometer (UV-Vis) and gas chromatography (GC) to check the optical properties and the photocatalytic results respectively. We make five different concentrations solutions of WO3 doping with Cu, and verify that doping improves the reaction activity successfully.
Research Purpose
- Yield regenerated energy from photocatalyst.
- Dope copper atom in WO3 with different concentrations.
- Analyze the result of the artificial photosynthesis.
Methodology
Conclusions and Future Work
- Doping Cu atoms enhance light absorption in visible spectrum and facilitate stronger ability of photocatalyst.
- WO3_Cu13 has been considered the most ideal doping concentration, whose electron consumption rate is 1.6 times higher than pristine WO3.
- Synthesize more different metal dopants and WO3 to find out the most efficient combination.
- Enhance the selectivity and efficiency of reaction to adopt the application in reality.